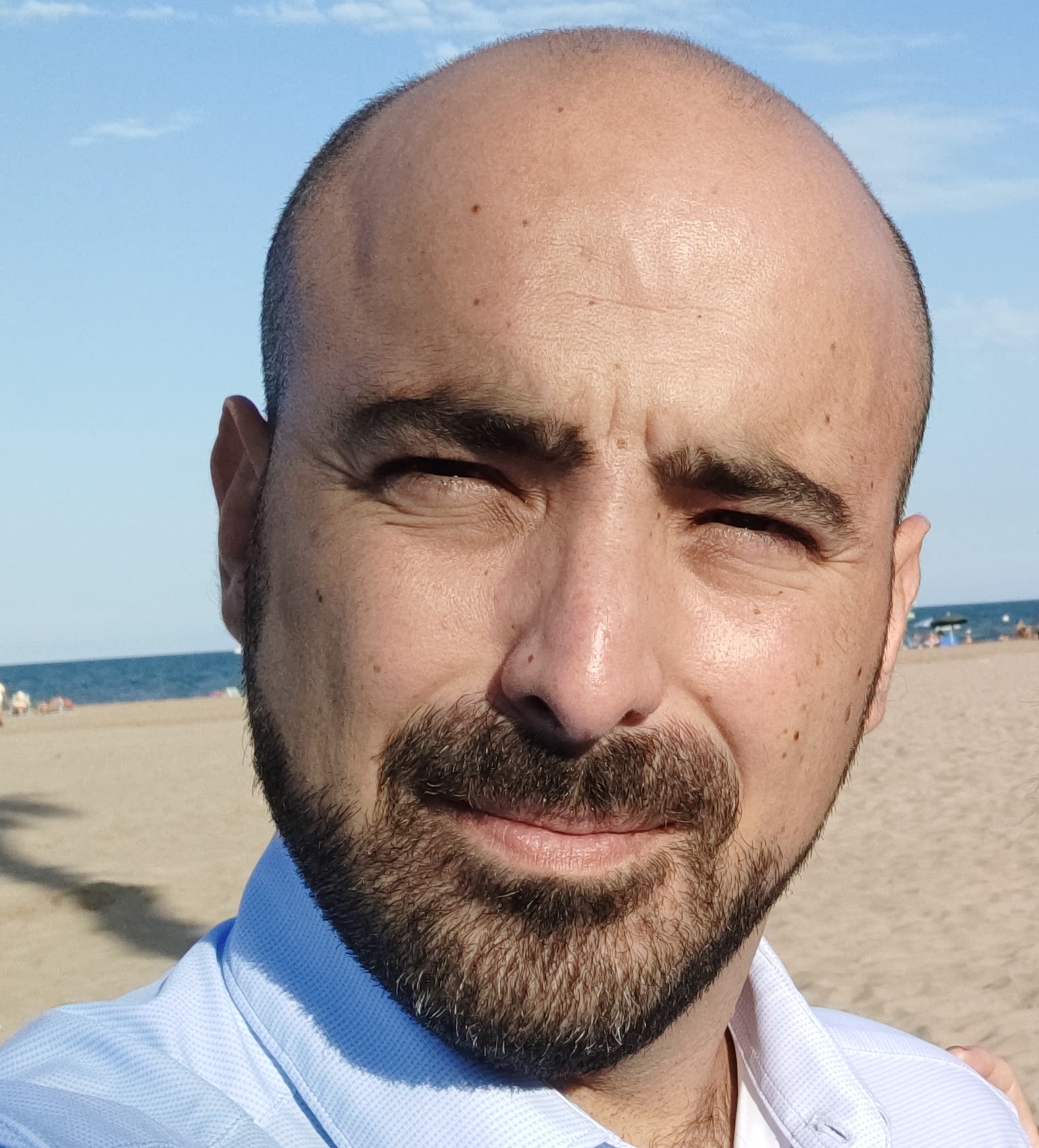
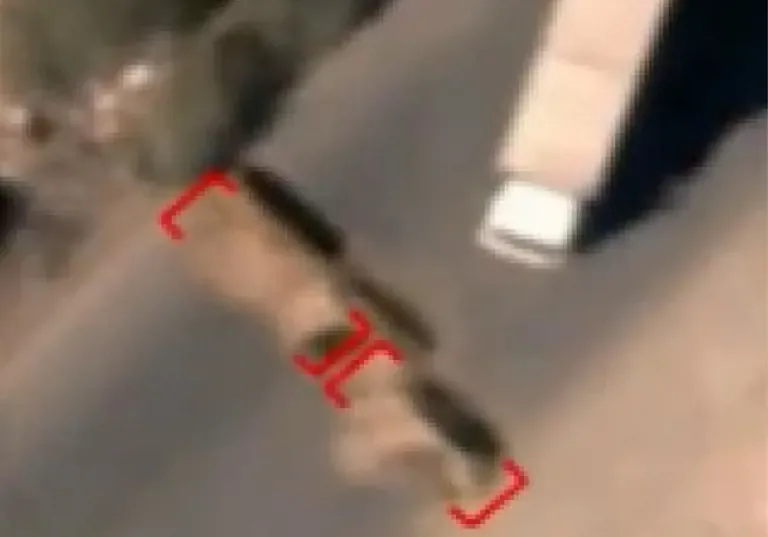
What happens when humanity dumps all sorts of toxic chemicals without any kind of environmental care or protection? We are talking about the Salton Sea. A large shallow saline lake located in the Coachella and Imperial Valleys of Southern California.
The Salton Sea was created by accident in 1905 when the Colorado River breached an irrigation canal, flooding the Salton Sink, a desert basin that lies below sea level. This inundation continued for two years, forming the sea as we know it today. It then became a popular tourist destination, known for boating, fishing and resort communities. Tourists flocked to its shores.
Nowadays it stays and remains as a barren Wateland. Clavero, a Spanish vlogger has taken the time to make a video about this, talking about it's effects. A small glimpse of what can happen when humanity uses an area of land without any kind of control, and a reminder of what can happen in many parts of the world that are following similar pollution build-ups.
The Salton Sea: California's forgotten Oasis
Nestled in the deserts of Southern California lies a remarkable and troubled body of water: the Salton Sea. Covering approximately 343 square miles, the Salton Sea holds the title of California's largest lake, yet it faces severe environmental challenges that threaten its very existence. In this blog post, we'll explore the Salton Sea's fascinating history, its current ecological crisis, and the efforts being made to save this unique and vital ecosystem.
A glimpse into history.
The Salton Sea's origins date back to 1905 when an engineering mishap caused the Colorado River to breach an irrigation canal, flooding the Salton Sink, a desert basin. This accidental inundation continued for two years, resulting in the formation of the Salton Sea. By the mid-20th century, this accidental lake had transformed into a bustling resort destination, drawing tourists for boating, fishing, and leisure.
Growing environmental crisis
Despite its past allure, the Salton Sea now grapples with severe environmental challenges:
- Rising Salinity: Without an outlet, the Salton Sea loses water only through evaporation, leading to skyrocketing salinity levels. It is now saltier than the Pacific Ocean, making it inhospitable for many fish species.
- Pollution: Runoff from nearby agricultural fields introduces pesticides, fertilizers, and other pollutants into the sea, exacerbating its ecological decline.
- Air Quality: As the sea's water level drops, vast stretches of lakebed are exposed. Winds whip up this exposed playa, releasing fine dust laced with toxic chemicals, contributing to poor air quality and respiratory issues in surrounding communities.
The path to restoring the Salton Sea is fraught with challenges, including securing funding, managing water resources, and balancing agricultural needs with environmental goals. Proposed solutions range from importing water from the Sea of Cortez to developing renewable energy projects like geothermal plants in the region.